
Anatomy
Central Nervous System
Which of the following clinical features is most suggestive of a lesion of the parietal lobe:
Answer:
Hemispatial sensory neglect is most likely to be associated with damage to the parietal lobe. Receptive dysphasia may be seen in damage to the Wernicke speech area in the temporal lobe. Expressive dysphasia may be seen in damage to the Broca speech area in the frontal lobe. Contralateral motor weakness is due to damage of the motor cortex of the frontal lobe. Homonymous hemianopia is most likely to occur in damage of the occipital lobe.Parietal Lobe
Anatomy / Central Nervous System
Last Updated: 6th November 2019
The parietal lobe lies between the frontal lobe anteriorly and the occipital lobe posteriorly, from which it is separated by the central sulcus and parieto-occipital sulcus, respectively. It sits superiorly in relation to the temporal lobe, being separated by the lateral sulcus.
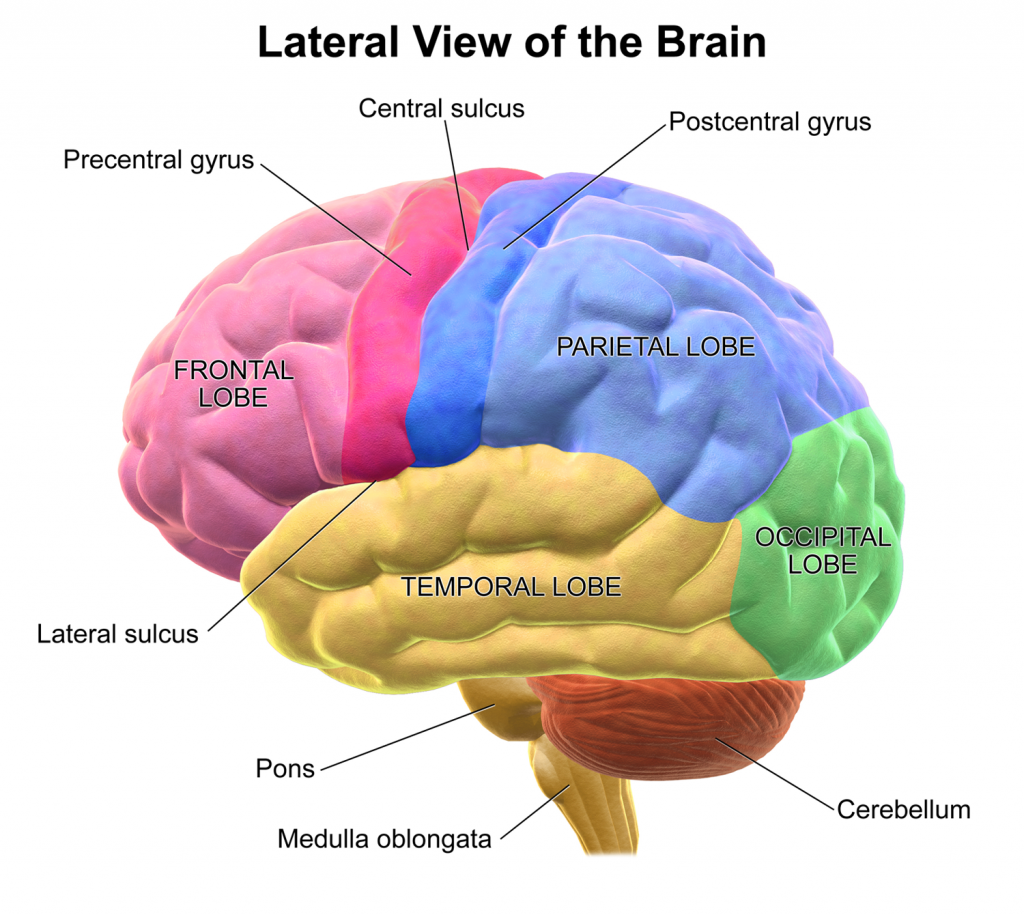
Lobes of the Brain. (Image by BruceBlaus (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Function
Areas of the parietal lobe are responsible for:
- Perceiving and interpreting sensation and proprioception
- Language and calculation of numbers on the dominant hemisphere side
- Integration of somatosensory, visual and auditory information and processing of visuospatial functions (e.g. 2-point discrimination) on the non-dominant hemisphere side
Cortical Areas
| Area | Function | Lesion |
|---|---|---|
| Primary somatosensory cortex and somatosensory association cortex | Sensation and proprioception, visuo-spatial perception | Loss of sensation, difficulty distinguishing left from right, sensory neglect, apraxia, loss of hand-eye coordination, tactile agnosia |
| Arcuate fasciculus | Connects audiovisual association areas with Broca and Wernicke speech areas | Difficulties with reading, writing, naming, maths |
| Optic radiation | Carries visual information to primary visual cortex | Contralateral homonymous inferior quadrantanopia |
- The primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus and is concerned with perceiving complex somatosensory stimuli from the contralateral side of the face and body. Together with the somatosensory association cortex, these areas are responsible for sensation and proprioception, and visuo-spatial perception.
- Pathways within the arcuate fasciculus are concerned with language as they connect Broca's area (frontal lobe) with Wernicke's area (temporal lobe).
- The fibres of the upper part of the optic radiation (serving the lower quadrant of the contralateral visual field) pass deep within the parietal lobe.
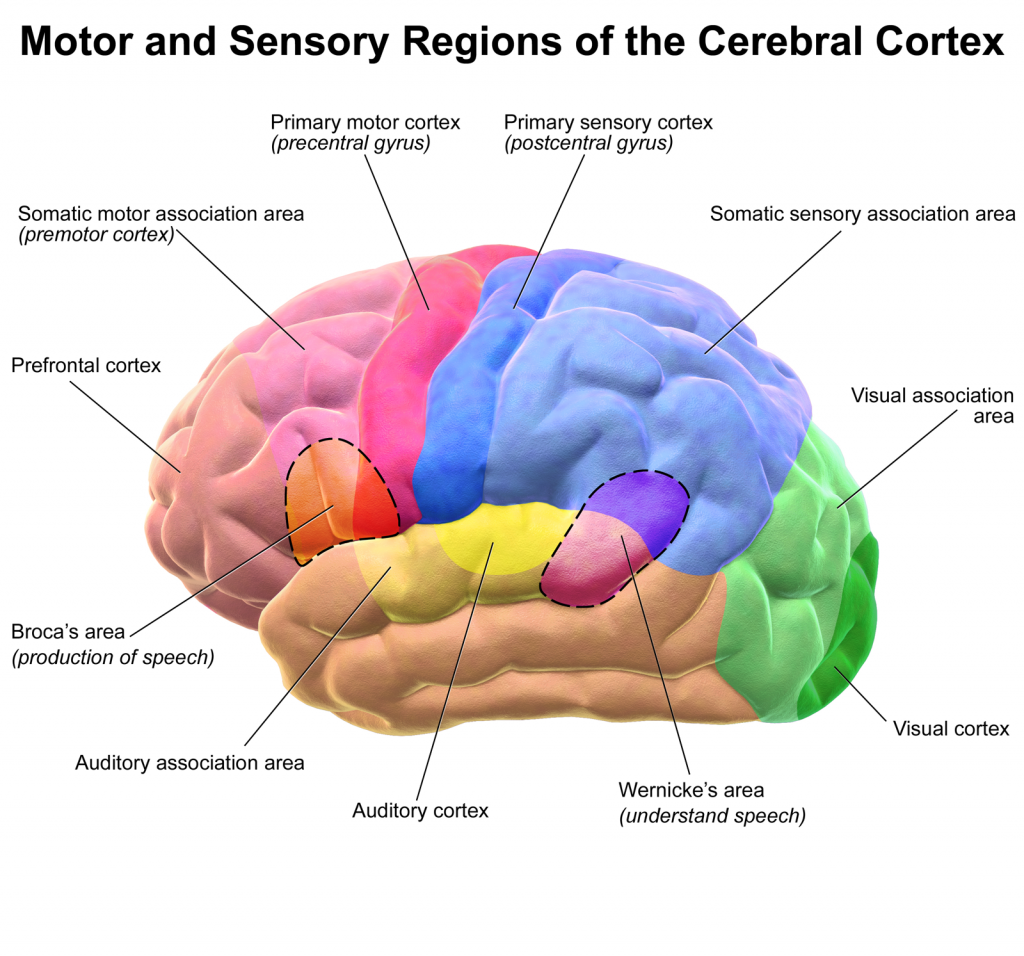
Motor and Sensory Regions of the Cerebral Cortex. (Image by Blausen.com staff. “Blausen gallery 2014, via Wikimedia Commons)
Blood Supply
The blood supply to the parietal lobe is from the middle cerebral artery.
![By derivative work: Frank Gaillard (talk) Brain_stem_normal_human.svg: Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Brain_stem_normal_human.svg) [GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or CC BY 2.5 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://primary-cdn.frcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Cerebral-Vascular-Territories-1-1.jpg)
Cerebral Blood Supply. (Image by derivative work: Frank Gaillard (talk) Brain_stem_normal_human.svg: Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Brain_stem_normal_human.svg) [GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), via Wikimedia Commons)
Clinical Implications:
Damage to the parietal lobe may result in:
- Cortical contralateral sensory loss with loss of proprioception and two-point discrimination
- Apraxia
- Tactile agnosia
- Attention deficits e.g. contralateral hemispatial neglect syndrome (an inability to perceive a contralateral stimulus when two simultaneous sensory stimuli are applied with equal intensity to corresponding sites on opposite sides of the body)
- Visual field defect (contralateral homonymous inferior quadrantanopia)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

