
Anatomy
Cranial Nerve Lesions
Which of the following nerves is the afferent pathway of the gag reflex:
Answer:
The glossopharyngeal nerve is the afferent pathway of the gag reflex. The vagus nerve is the efferent pathway of the gag reflex.Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Anatomy / Cranial Nerve Lesions / Head and Neck / Neck
Last Updated: 6th December 2020
The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) mediates taste, salivation and swallowing (together with CN X).
Table: Overview of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
| Cranial Nerve | Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) |
|---|---|
| Key anatomy | Originates from medulla, exits skull via jugular foramen |
| Sensory function | Posterior one-third of tongue, tonsils, oropharynx, soft palate, middle ear, taste from posterior one-third of tongue, visceral afferents from carotid body and sinus, afferent pathway of gag reflex |
| Motor function | Stylopharyngeus muscle (facilitates swallowing), parasympathetic fibres to parotid gland |
| Assessment | Gag reflex, swallowing |
| Clinical effects of injury | Loss of gag reflex, dysphagia, loss of carotid sinus reflex, loss of taste from posterior one-third of tongue |
| Causes of injury | Occipital condyle fractures, lateral medullary syndrome, jugular foramen syndrome, carotid artery dissection |
Anatomical Course
The glossopharyngeal nerve originates from the medulla and travels lateral in the posterior cranial fossa before emerging from the cranial cavity via the jugular foramen.
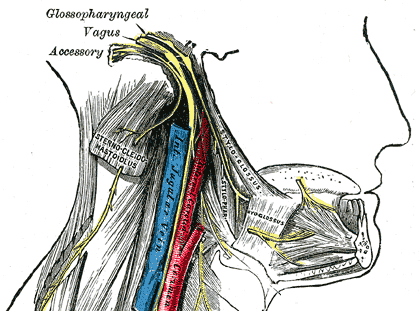
Glossopharyngeal Nerve. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Function
The glossopharyngeal nerve carries:
- General visceral afferent fibres from the carotid body and sinus
- General sensory afferent fibres from the posterior one-third of the tongue, palatine tonsils, oropharynx, and mucosa of the middle ear, pharyngotympanic tube and mastoid ear cells
- Special afferent fibres for taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue
- Parasympathetic secretomotor fibres to the parotid salivary gland
- Motor fibres to the stylopharyngeus muscle (elevates larynx and pharynx facilitating swallowing)
Assessment
The glossopharyngeal nerve can be assessed together with the vagus nerve (CN X) by:
- Asking the patient to cough
- Asking the patient to open the mouth wide and say 'ah' while visualising the palate and posterior pharyngeal wall (the soft palate should move upwards centrally)
- Testing the gag reflex
Likely Causes of Disease or Injury
Causes of damage to CN IX include:
- Occipital condyle fractures
- Lateral medullary syndrome
- Ischaemia secondary to vertebral artery damage
- Jugular foramen syndrome (palsy of CN IX, X, XI and XII caused by tumours, meningitis and infection from the middle ear spreading into the posterior fossa or trauma)
- Carotid artery dissection
Isolated glossopharyngeal nerve palsy is rare. It is usually damaged with CN X and XI, close to the jugular foramen.
Common Clinical Effects
CN IX palsy will result in:
- Loss of gag reflex (afferent pathway)
- Loss of carotid sinus reflex
- Loss of taste from posterior one-third of tongue
- Dysphagia
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

