
Anatomy
Abdomen
Pain from the rectum is carried to which of the following spinal cord levels:
Answer:
Visceral afferent fibres from the rectum follow the parasympathetic supply to the S2 - S4 spinal sensory ganglia.Rectum
Anatomy / Abdomen / Gastrointestinal Tract
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The rectum is continuous above with the sigmoid colon at the rectosigmoid junction at about the level of vertebra S3, where the sigmoid mesocolon ends, and below with the anal canal as this structure penetrates the pelvic floor to enter the perineum. The lower part of the rectum is expanded to form the rectal ampulla.
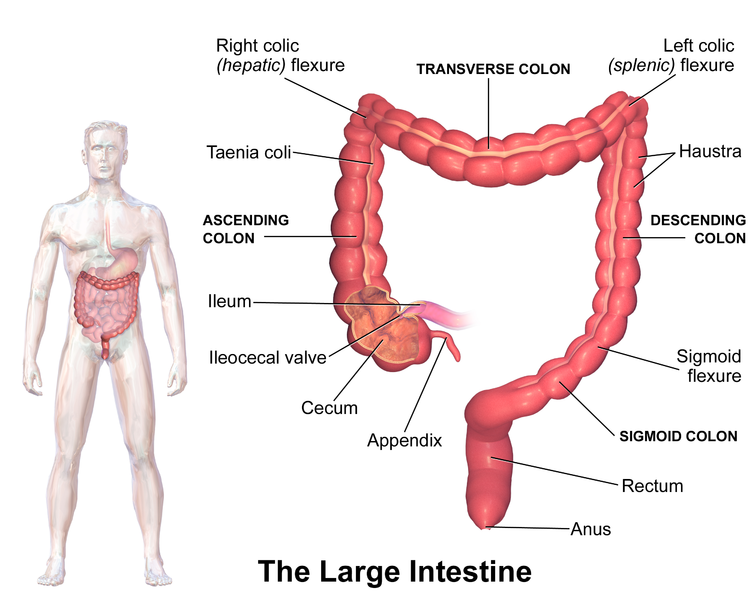
Large Intestine. (Image by Blausen.com staff. “Blausen gallery 2014”. Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 20018762. (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Relations
The rectum is a retroperitoneal structure. It is the most posterior viscera in the pelvic cavity, lying immediately anterior to, and following the concave contour of the sacrum.
The rectum lies posterior to the bladder, prostate and seminal vesicle in men and to the uterus, vagina and cervix in women.
In men, the rectovesical septum lies between the fundus of the bladder and the ampulla of the rectum and is closely associated with the seminal glands and prostate. In females, the rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas) is a peritoneal recess between the rectum and uterus.

Relations of the Rectum. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Digital Rectal Examination
In a PR/DRE the following structures may be palpated through the anterior rectal wall:
- the vagina, cervix and retroverted uterus in women
- the prostate, seminal vesicle and base of the urinary bladder in men
The bony structures that are palpated through the posterior rectal wall are the anterior surface of the lower sacrum and coccyx and the ischial spine and tuberosity.
The anal mucosa and rectal walls themselves are also examined.

Digital Rectal Examination (Image by Unknown Illustrator [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Innervation
Sympathetic nervous supply to the rectum is from the lumbar splanchnic nerves (L1, L2) and the inferior mesenteric plexus (upper rectum) and hypogastric plexuses (middle and lower rectum).
Parasympathetic supply is from the pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2 - S4) and inferior hypogastric plexus.
Visceral afferent fibres follow the parasympathetic supply to the S2 - S4 spinal sensory ganglia.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

