
Physiology
Cardiovascular
Which of the following type of blood vessel contributes the most to total peripheral resistance:
Answer:
The major regulator of vascular resistance in the body is regulation of vessel radius. In humans, there is very little pressure change as blood flows from the aorta to the large arteries, but the small arteries and arterioles are the site of about 70% of the pressure drop, and are the main regulators of total peripheral resistance. Smaller arteries and arterioles contain relatively more muscle and are resistance vessels, responsible for controlling tissue blood flow through constriction.Vascular System Structure
Physiology / Cardiovascular / Peripheral Vascular System
Last Updated: 29th July 2024
The vascular system consists of arteries and arterioles that take blood from the heart to the tissues, thin-walled capillaries and postcapillary venules that allow the diffusion of gases and metabolites, and venules and veins that return blood to the heart. The blood pressure, vessel diameter and wall thickness vary throughout the circulation. Varying amounts of smooth muscle are contained within the vessel walls, allowing them to constrict and alter their resistance to flow.
Arteries and Arterioles
Large arteries are elastic and partially damp out oscillations in pressure produced by pumping of the heart; stiff arteries (e.g. age, atherosclerosis) result in larger oscillations. The major arteries are conductance vessels and divide repeatedly into smaller muscular arterioles.
Smaller arteries and arterioles contain relatively more muscle and are resistance vessels, responsible for controlling tissue blood flow through constriction. Each small arteriole feeds many capillaries via several terminal arterioles.
Microcirculation
The microcirculation consists of the terminal arterioles and the exchange vessels, the capillaries and small postcapillary venules, which have no smooth muscle or valves and which provide the exchange surface between blood and tissues.
Venules and Veins
Small venules rejoin into larger venules which ultimately drain into veins. Veins have a larger diameter than equivalent arteries and provide less resistance. They have thin distensible walls and contain about 70% of the total blood volume at any one time.
Large veins are capacitance vessels and act as a blood volume reservoir; when required they can constrict and increase the effective blood volume. Large veins in the limbs contain one-way valves, and when muscle activity intermittently compresses these veins, they act as a pump and assist venous return to the heart.
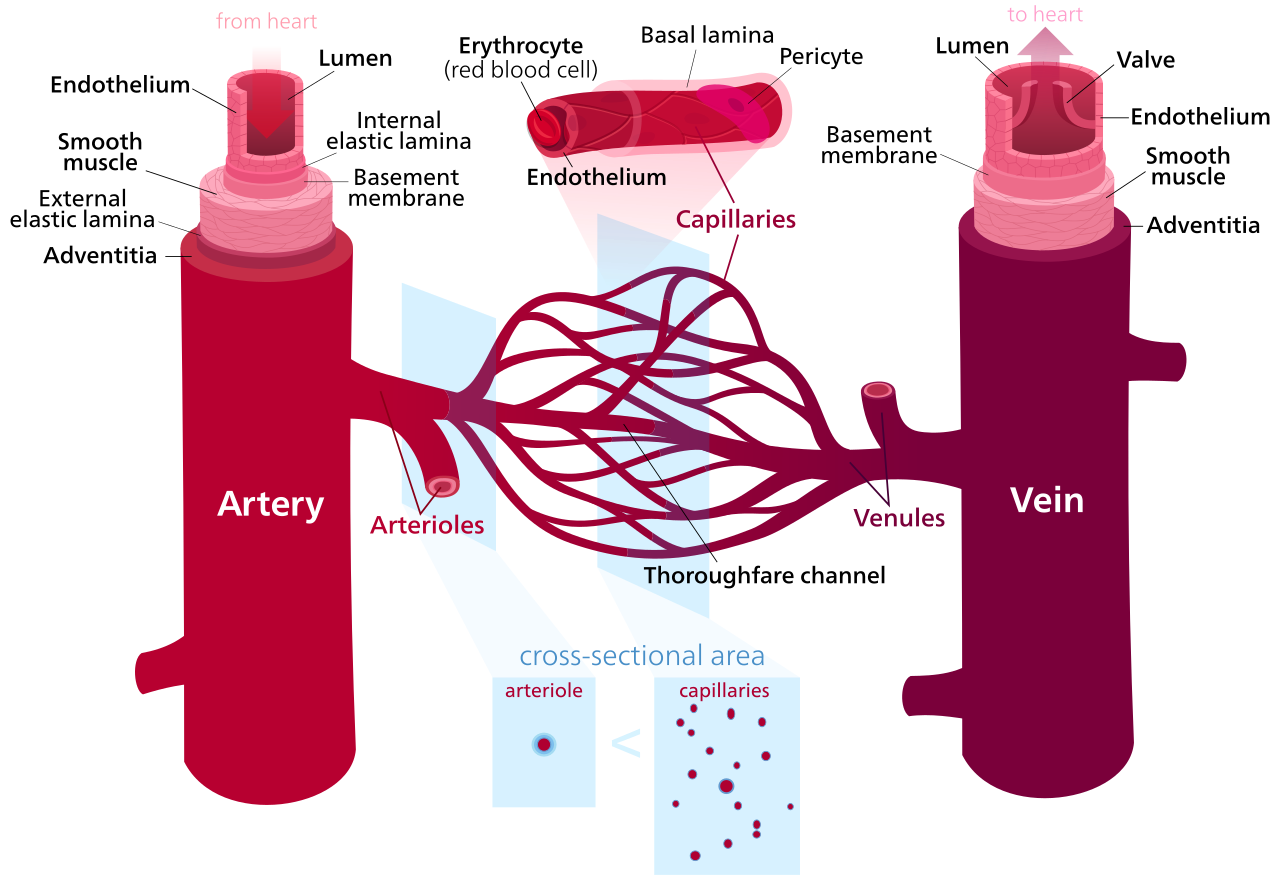
Overview of the Vascular System. (Image by Kelvinsong (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

