
Anatomy
Thorax
A 35 year old woman is brought to ED having been involved in a road traffic accident. She has sustained a chest injury on impact with the steering wheel and fractured the sternum at the manubriosternal joint. Which of the following ribs would most likely also be involved in this injury:
Answer:
The first rib articulates with the manubrium of the sternum forming the anterior border of the thoracic inlet. The second rib articulates with the sternum at the manubriosternal joint (the sternal angle).There are twelve pairs of ribs, each terminating anteriorly in a costal cartilage.
True and False Ribs
The ribs are divided into 'true' and 'false' ribs based on their anterior attachments:
- The true ribs (1 - 7) attach directly to the sternum anteriorly.
- The false ribs (8 - 12) can be further divided into those that attach to the costal cartilage of the rib above them (8 - 10) and the floating ribs (11 + 12) that do not have any anterior attachments.
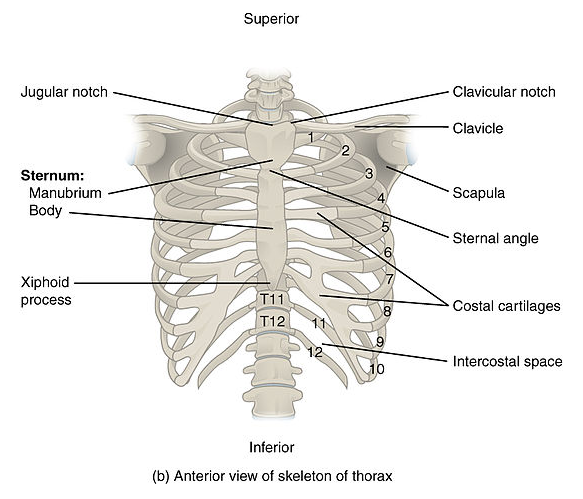
Anterior Rib Joints. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons)
Posterior Joints
Posteriorly, all of the ribs articulate with the thoracic vertebrae of the spine.
Each typical rib forms two joints posteriorly:
- the costotransverse joint (between the tubercle of the rib and the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra)
- the costovertebral joint (between the two facets on the head of the rib and the superior costal facet on the body of the corresponding vertebra, and the inferior costal facet on the body of the vertebra above).
![Modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Rib-joint.png)
Posterior Rib Joints. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Typical Ribs
The typical rib consists of a head, a neck and a body:
- The head of the rib has two articular facets which articulate with the superior costal facet on the body of the corresponding vertebra, and the inferior costal facet on the body of the vertebra above.
- The neck of the rib connects the head to the body. Where the neck meets the body, there is a tubercle which articulates with the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra.
- The body of the rib is flat and curved.
The inferior margin of the internal surface of the body is marked by the costal groove which protects the neurovascular structures which run within it.
![Modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://primary-cdn.frcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Rib.gif)
Typical Rib. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Atypical Ribs
Table: Distinguishing Features of the Atypical Ribs
| Atypical Rib | Distinguishing Features |
|---|---|
| Rib 1 | Shorter and wider, single facet for articulation with T1, scalene tubercle |
| Rib 2 | Flat, roughened area for attachment of serratus anterior muscle |
| Rib 10 | Single facet for articulation with T10 |
| Rib 11 | No neck, single facet for articulation with T11 |
| Rib 12 | No neck, single facet for articulation with T12 |
The atypical ribs consist of ribs 1, 2, 10, 11 and 12.
- Rib 1 is shorter and wider than the other ribs. The head of rib 1 has only one facet for articulation with the body of its own vertebra (T1); it does NOT articulate with vertebrae C7. The superior surface of rib 1 is characterised by the scalene tubercle about midway along the body, which separates two smooth grooves in the rib made by the subclavian vein anteriorly and the subclavian artery posteriorly.
- Like rib 1, rib 2 is flat but twice as long. It has a roughened area on its upper surface where the serratus anterior muscle attaches.
- The head of rib 10 only has a single facet for articulation with the body of its own vertebra (T10).
- Ribs 11 and 12 have no neck, and have only one facet for articulation with the bodies of their own vertebrae (T11 and T12).
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

