
Anatomy
Head and Neck
A 34 year old woman presents to ED complaining of a hoarse voice. She underwent a thyroidectomy 2 weeks ago. Which of the following nerves was most likely injured during the procedure:
Answer:
The thyroid gland and the recurrent laryngeal nerve are in close proximity and thus this nerve is most likely injured in thyroid surgery. The recurrent laryngeal nerve supplies most of the motor innervation to the larynx and sensation below the true vocal folds.Thyroid Gland
Anatomy / Head and Neck / Neck
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The thyroid gland is anterior in the neck, below and lateral to the thyroid cartilage, and spanning between the C5 and T1 vertebrae.
It has two lateral lobes (which cover the anterolateral surfaces of the trachea, cricoid cartilage and the lower part of the thyroid cartilage) connected by the isthmus which crosses the anterior surface of the second and third tracheal cartilages.
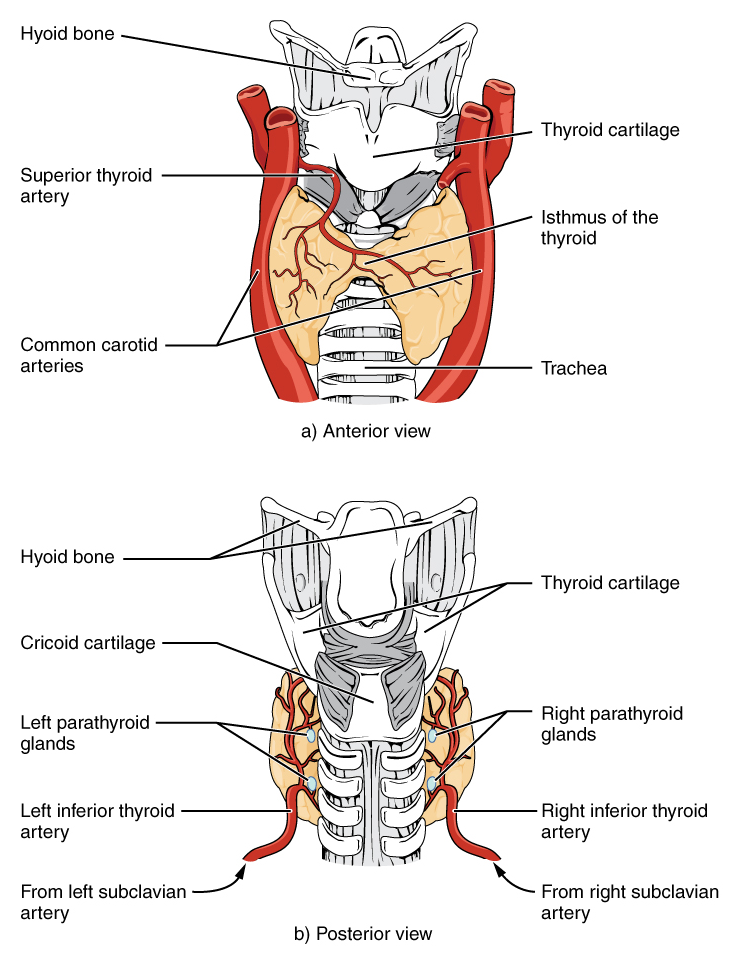
Thyroid Gland. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons)
Relations
It lies deep to the sternohyoid, sternothyroid and omohyoid muscles, in the visceral compartment of the neck, together with and anterior to the pharynx, trachea and oesophagus, and surrounded by the pretracheal fascia.
Structures vulnerable in thyroid surgery include:
- Thyroidea ima artery
- Inferior thyroid vein
- Anterior jugular vein
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Cervical dome of the pleura
- Oesophagus
- Parathyroid glands
Blood Supply
The thyroid gland is supplied predominantly by the superior thyroid artery (branch of the external carotid artery) and the inferior thyroid artery (branch of the thyrocervical trunk from the subclavian artery). Occasionally a small thyroidea ima artery arises from the brachiocephalic trunk or the arch of the aorta and ascends to supply the thyroid gland.
Venous Drainage
The venous drainage of the thyroid is to the superior and middle thyroid veins (draining to the internal jugular vein) and the inferior thyroid veins (draining to the brachiocephalic veins).
Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland is to nodes beside the trachea (paratracheal nodes) and to deep cervical nodes inferior to the omohyoid muscle along the internal jugular vein.
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
The thyroid gland is closely related to the recurrent laryngeal nerves. After branching from the vagus nerve and looping around the subclavian artery on the right and the arch of the aorta on the left, the recurrent laryngeal nerves ascend in the neck in a groove between the trachea and oesophagus. They pass deep to the posteromedial surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland and enter the larynx by passing deep to the lower margin of the inferior constrictor of the pharynx.
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is the most commonly injured nerve during thyroid surgery. The recurrent laryngeal nerves supply sensory innervation to the laryngeal cavity below the level of the vocal folds and motor innervation to all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except for the cricothyroid muscle.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

