
Anatomy
Head and Neck
The sensory innervation of the nasopharynx is provided by which of the following nerves:
Answer:
Each subdivision of the pharynx has a different sensory innervation:- the nasopharynx is innervated by the maxillary nerve
- the oropharynx is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve
- the laryngopharynx is innervated by the vagus nerve.
Pharynx
Anatomy / Head and Neck / Pharynx
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The pharynx is a musculofascial structure that connects the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and the oesophagus in the neck.
Anatomical Location
The pharynx is attached above to the base of the skull, and is continuous below, approximately at the level of vertebra C6, with the top of the oesophagus.
The pharynx is separated from the posterior vertebral column by a thin retropharyngeal space, bordered anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia and posteriorly by the prevertebral fascia.
![By OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://primary-cdn.frcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/pharynx-1024x855.jpg)
Relations of the Pharynx. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons)
Arrangement
The walls of the pharynx are attached anteriorly to the margins of the nasal cavities, oral cavity and larynx, dividing the pharynx into the continuous nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx respectively.
The posterior apertures of the nasal cavities open into the nasopharynx, the oropharyngeal isthmus opens into the oropharynx and the superior aperture of the larynx opens into the laryngopharynx.
The pharyngotympanic tubes (from the middle ear) open into the lateral walls of the nasopharynx.
Muscles
The muscles of the pharyngeal wall are organised into two groups:
- The three sheet-like constrictor muscles constrict the pharyngeal cavity sequentially to move a bolus of food through the pharynx and into the oesophagus during swallowing.
- The three longitudinal muscles elevate the pharyngeal wall, or during swallowing, pull the pharyngeal wall up and over a bolus of food being moved through the pharynx into the oesophagus.
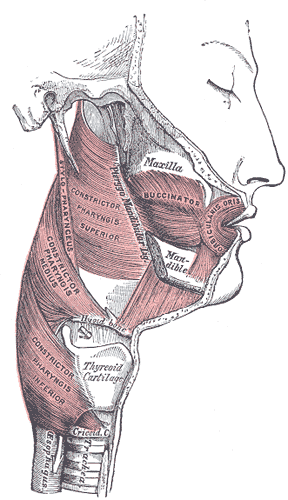
Muscles of the Pharynx. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Innervation
The muscles of the pharynx are all innervated by the vagus nerve except for the stylopharyngeus muscle, innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve. The branches of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves form a pharyngeal plexus in the outer fascia of the pharyngeal wall.
Each subdivision of the pharynx has a different sensory innervation:
- the nasopharynx is innervated by the maxillary nerve
- the oropharynx is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve
- the laryngopharynx is innervated by the vagus nerve
Thus the glossopharyngeal nerve is the afferent pathway of the gag reflex and the vagus nerve is the efferent pathway.
Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic vessels from the pharynx drain into the deep cervical lymph nodes.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

