
Anatomy
Lower Limb
A 21 year old man presents to ED complaining of numbness over the dorsum of his left foot and inability to dorsiflex or evert his foot. He has had a knee-high plaster cast on his left leg for the past 5 weeks. Which of the following is the most likely site of nerve compression that has resulted in his symptoms:
Answer:
Dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot are primarily produced by the anterior compartment and the lateral compartment of the leg, innervated by the deep fibular nerve and the superficial fibular nerve respectively. Sensation over the dorsum of the foot is primarily supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. The common fibular nerve is susceptible to injury where it wraps around the neck of the fibula when passing from the popliteal fossa into the leg. This may occur by impact injuries, fractures to the bone or leg casts that are placed too high.Common Fibular Nerve
Anatomy / Lower Limb / Innervation of Lower Limb / Popliteal Fossa and Knee
Last Updated: 23rd May 2025
The common fibular nerve, also known as the common peroneal nerve, is a branch of the sciatic nerve receiving fibres from L4 - S2.
Table: Anatomical Overview of the Common Fibular Nerve
| Nerve | Common Fibular |
|---|---|
| Nerve roots | L4 – S2 |
| Motor supply | Directly: Short head of the biceps femoris
Terminal Branches: All muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg, all intrinsic dorsal foot muscles |
| Sensory supply | Directly: Skin over the upper lateral leg
Terminal Branches: Skin over the lateral aspect of the lower leg and ankle, and dorsal aspect of the foot and toes (except for the lateral side of little toe) |
| Injury | Motor Loss: Loss of dorsiflexion of ankle and foot eversion, weakness of foot inversion, loss of toe extension, foot drop with high-stepping gait and loss of sensation in above distribution
Sensory Loss: Loss of sensation in skin over the lateral aspect of leg and ankle, and dorsal aspect of the foot and toes (except for the lateral side of little toe) |
Anatomical Course
The nerve arises at the apex of the popliteal fossa and follows the medial margin of the biceps femoris tendon over the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. Here it gives rise to two cutaneous branches, the sural communicating nerve which joins the sural nerve (branch of the tibial nerve), and the lateral sural cutaneous nerve (supplying skin over the upper lateral leg).
The common fibular nerve continues by wrapping around the neck of the fibula and passing between the attachments of the fibularis longus muscle to enter the lateral compartment of the leg where it divides into its terminal branches, the superficial and deep fibular nerves.
![By Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Sciatic-Nerve.png)
Common Fibular Nerve. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
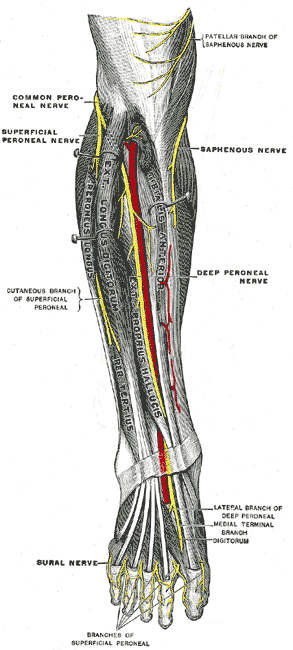
Superficial Fibular Nerve. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Branches
Table: Branches of the Common Fibular Nerve
| Branch | Supply |
|---|---|
| Muscular branch | Short head of biceps femoris muscle |
| Sural communicating nerve | Joins sural nerve |
| Lateral sural cutaneous nerve | Skin over upper lateral leg |
| Superficial fibular nerve | Lateral compartment of leg and skin over lower anterolateral leg, and dorsum of foot (except lateral side of little toe and skin over webspace of 1st and 2nd toe) |
| Deep fibular nerve | Anterior compartment of leg and skin over webspace between 1st and 2nd toes |
Function
The common fibular nerve directly innervates the short head of the biceps femoris muscle and supplies skin over the upper lateral leg via its lateral sural cutaneous branch.
Through its terminal branches, the common fibular nerve innervates all of the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and the dorsal intrinsic foot muscles and skin over the anterolateral aspect of the lower leg and the dorsal aspect of the foot and toes (except for the lateral side of the little toe, supplied by the sural branch of the tibial nerve).
Table: Motor Supply of the Common Fibular Nerve
| Muscle | Function | Branch |
|---|---|---|
| Tibialis anterior | Dorsiflexion and inversion of foot, support of medial arch of foot | Deep fibular nerve |
| Extensor hallucis longus | Extension of great toe and dorsiflexion of foot | Deep fibular nerve |
| Extensor digitorum longus | Extension of lateral four toes and dorsiflexion of foot | Deep fibular nerve |
| Fibularis tertius | Dorsiflexion and eversion of foot | Deep fibular nerve |
| Fibularis longus | Plantarflexion and eversion of foot, support of lateral and transverse arch | Superficial fibular nerve |
| Fibularis brevis | Eversion of foot | Superficial fibular nerve |
![Modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Cutaneous-Innervation-Leg.png)
Cutaneous Innervation of Lower Limb. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

