
Anatomy
Head and Neck
Regarding the larynx, which of the following statements is INCORRECT:
Answer:
The intrinsic muscles alter the size and shape of the laryngeal inlet and move the vocal folds. The extrinsic muscles are involved in elevation and depression of the larynx to produce swallowing.Larynx Muscles
Anatomy / Head and Neck / Larynx
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The larynx is suspended from the superior hyoid bone and attached to the trachea below by membranes and ligaments. It opens above into the pharynx immediately posterior and slightly inferior to the tongue and the oropharyngeal isthmus of the oral cavity, and blends inferiorly with the trachea at the vertebral level C6.
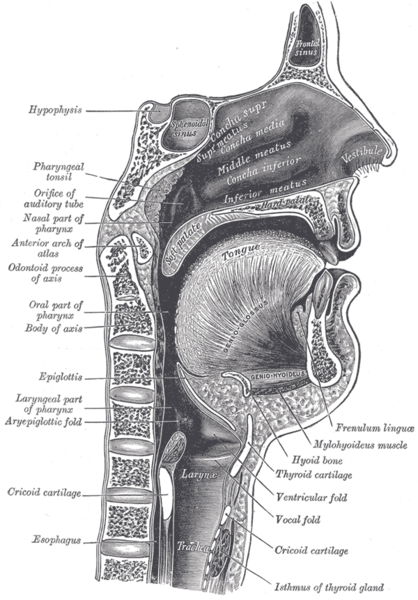
Relations of the Larynx. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain])
Function
There are four principal roles of the larynx:
- phonation
- sphincteric to close the lower respiratory tract (for example during swallowing)
- coughing
- breath-holding while straining (vocal cord adduction).
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Muscles
The laryngeal muscles are divided into intrinsic and extrinsic groups.
The intrinsic muscles alter the size and shape of the laryngeal inlet and move the vocal folds.
The extrinsic muscles are involved in elevation and depression of the larynx to produce swallowing.

Vocal Cords. (Image by Unknown [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Innervation
Motor and sensory innervation of the larynx is provided by the vagus nerve via its superior laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal branches.
The recurrent laryngeal nerves are sensory to the laryngeal cavity below the level of the vocal folds and motor to all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except for the cricothyroid muscle (innervated by the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve).
A lesion of the recurrent laryngeal nerve may cause respiratory obstruction, hoarseness, inability to speak and loss of sensation below the vocal cord.
The superior laryngeal nerve supplies sensation to the mucous membrane above the vocal cord and the taste buds on the epiglottis, and motor innervation to the cricothyroid and the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles.
A lesion of the superior laryngeal nerve may cause loss of sensation above the vocal cord and taste on the epiglottis, and a weak hoarse voice.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

