
Anatomy
Abdomen
The sacrotuberous ligament spans between which of the following structures:
Answer:
The sacrotuberous ligament is also triangular with its apex attached to the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity and its broad base attached to the posterior superior iliac spine of the pelvic bone along the dorsal aspect and lateral margin of the sacrum, and onto the dorsolateral surface of the coccyx.Bony Pelvis
Anatomy / Abdomen / Pelvic Cavity
Last Updated: 21st September 2020
The bones of the pelvis consist of the right and left pelvic bones, the sacrum and the coccyx.
Each pelvic bone is formed by three elements: the ilium (superiorly), the pubis (anteroinferiorly) and the ischium (posteroinferiorly). The lateral surface of the pelvic bone has a large articular socket, the acetabulum, which together with the head of the femur, forms the hip joint.
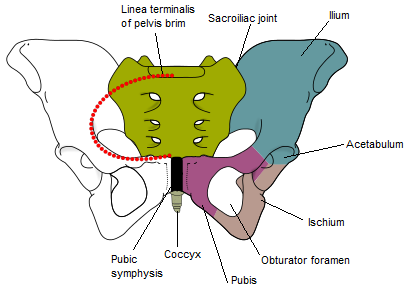
Bones of the Pelvis. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Fred the Oyster [CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Articulations
- The pelvic bones articulate posteriorly with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joints and with each other anteriorly at the pubic symphysis.
- The sacroiliac joints are stabilised by three ligaments; the anterior, interosseous and posterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- The pubic symphysis is stabilised by two major ligaments; the superior and inferior pubic ligaments.
- The sacrum articulates superiorly with vertebra L5 at the lumbosacral joints and inferiorly with the coccyx at the sacrococcygeal joint.
- The lumbosacral joints are reinforced by strong iliolumbar and lumbosacral ligaments that extend from the expanded transverse processes of vertebra L5 to the ilium and the sacrum respectively.
- The sacrococcygeal joint is stabilised by a series of sacrococcygeal ligaments.
Sacrospinous and Sacrotuberous Ligaments
The sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments are major components of the lateral pelvic walls.
The sacrospinous ligament is triangular with its apex attached to the ischial spine and its base attached to the related margins of the sacrum and coccyx.
The sacrotuberous ligament is also triangular with its apex attached to the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity and its broad base attached to the posterior superior iliac spine of the pelvic bone along the dorsal aspect and lateral margin of the sacrum, and onto the dorsolateral surface of the coccyx.
These ligaments stabilise the sacrum on the pelvic bones by resisting the upward tilting of the inferior aspect of the sacrum. They also convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches of the pelvic bone into the greater foramina (superior to the sacrospinous ligament and ischial spine) and lesser foramina (inferior to the sacrospinous ligament and between the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament).
![Modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Pelvis3-1.png)
Sacrospinous Ligament (purple) and Sacrotuberous Ligament (blue). (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

