
Anatomy
Abdomen
A 65 year old lady complains of faecal incontinence. Dysfunction of which of the following structures is most likely a contributing factor to her symptoms:
Answer:
The levator ani muscle consists of two major portions , the pubococcygeus and iliococcygeus, which help support the pelvic viscera and resist increases in intra- abdominal pressure. The puborectalis is the most medial and inferior portion of the pubococcygeus which forms a loop around the anorectal junction which helps maintain an anorectal angle at around 90 degrees. To facilitate defaecation, the puborectalis muscle relaxes, decreasing the angle between the ampulla of the rectum and the upper portion of the anal canal.Anal Canal
Anatomy / Abdomen / Gastrointestinal Tract
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The anal canal is the last 4 cm of the adult gastrointestinal tract and begins at the terminal end of the rectal ampulla, where it narrows at the pelvic floor. The anal canal is divided into the upper two-thirds and the lower one-third by the pectinate (dentate) line.
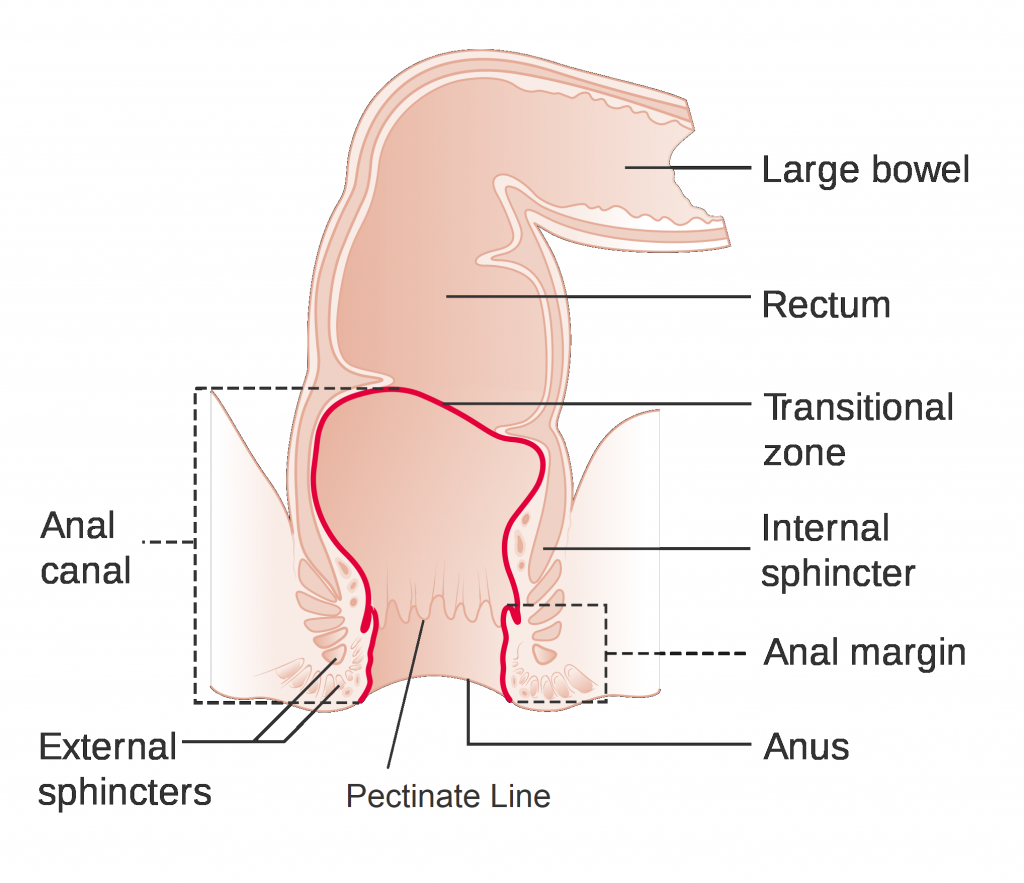
Anal Canal. (Image by Cancer Research UK [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons)
Anatomical Position
The anorectal junction is pulled forward by the action of the puborectalis muscle (part of the levator ani muscle) and so the anal canal moves in a posterior direction as it passes inferiorly through the pelvic floor.
As it passes through the pelvic floor, it is surrounded along its entire length by the internal anal sphincter (involuntary) and external anal sphincter (voluntary), which normally keep it closed.
The anal canal terminates as the anus after passing through the perineum.
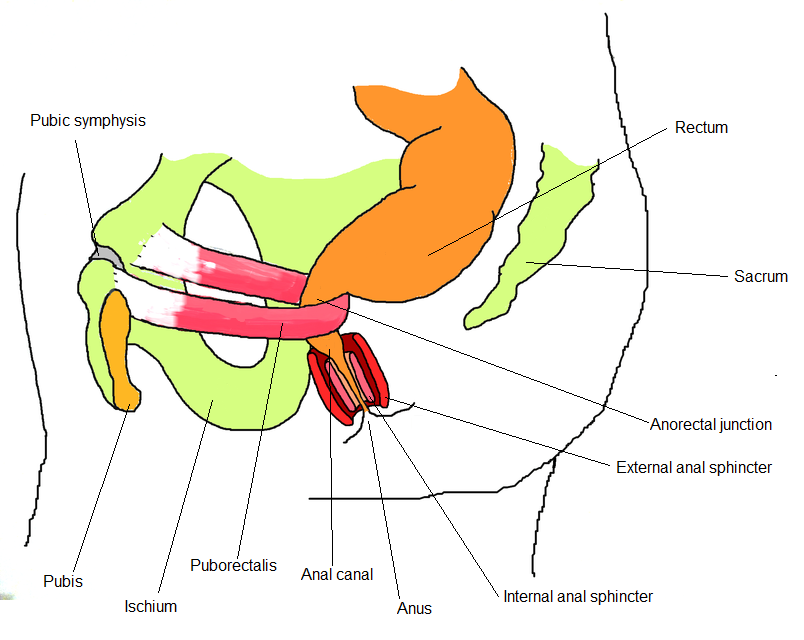
Relations of the Anal Canal. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Unknown [CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Control of Defecation
Defecation is initiated by distension of the rectal ampulla which activates visceral afferent impulses transmitted to the spinal cord by the pelvic splanchnic nerve. Parasympathetic stimulation increases peristalsis and relaxes the internal anal sphincter, facilitating defecation. Sympathetic stimulation causes a decrease in peristalsis, and maintains tone in the internal anal sphincter, inhibiting defecation.
To facilitate defecation:
- Intra-abdominal pressure is increased by breath-holding and contracting the diaphragm and the abdominal muscles
- The puborectalis muscle relaxes, decreasing the angle between the ampulla of the rectum and the upper portion of the anal canal
- The smooth muscle in the wall of the rectum contracts, the internal anal sphincter relaxes, and the external anal sphincter relaxes
Lymphatic Drainage
Above the pectinate line, the anal canal drains to the internal iliac lymph nodes which subsequently drain to the lumbar (para-aortic) nodes.
Below the pectinate line, the anal canal drains to the superficial inguinal nodes. These nodes have efferent vessels that drain primarily into the external iliac nodes and ultimately to the lumbar (para-aortic) nodes.
Innervation
Above the pectinate line, the anal canal receives innervation from the autonomic nervous system via the inferior hypogastric plexus.
Below the pectinate line it is innervated by the somatic fibres of the pudendal nerve (S2 - S4) which also innervates the external anal sphincter and most of the skin over the perineum.
The anococcygeal nerves originate from the coccygeal plexus (S4 - C0) and innervate skin in the anal triangle of the perineum.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

