
Anatomy
Abdomen
The inguinal ligament is formed from which of the following:
Answer:
The lower free border of the external oblique aponeurosis forms the inguinal ligament on each side (which runs between the anterior superior iliac spine laterally and the pubic tubercle medially).Anterior Abdominal Wall Muscles
Anatomy / Abdomen / Anterior Abdominal Wall
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
There are five muscles in the anterolateral group of abdominal wall muscles; three flat muscles whose fibres begin posterolaterally and pass anteriorly before being replaced by an aponeurosis as the muscle continues towards the midline (external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis) and two vertical muscles enclosed by the tendinous sheath formed by the aponeuroses of the flat muscles (rectus abdominis, pyramidalis).
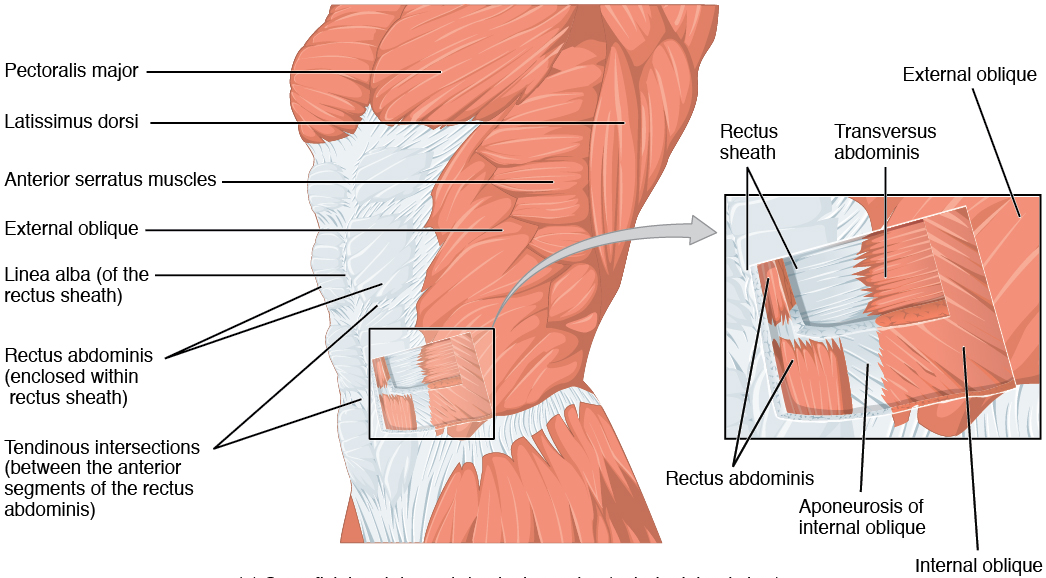
Anterior Abdominal Wall Muscles. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons)
External oblique
The external oblique is the largest and most superficial of the anterior abdominal muscles, lying just deep to the superficial fascia. The external oblique originates from the outer surfaces of the lower eight ribs, its fibres running in an inferomedial direction before inserting onto the lateral lip of the iliac crest.
The external oblique has a large aponeurotic component that covers the anterior part of the abdominal wall and forms the linea alba at the midline, together with the aponeuroses from the internal oblique and the transversus abdominis. The linea alba extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis.
The lower free border of the external oblique aponeurosis forms the inguinal ligament on each side (which runs between the anterior superior iliac spine laterally and the pubic tubercle medially).
Internal oblique
The internal oblique muscle lies deep to the external oblique. Its fibres run in a superomedial direction, originating from the thoracolumbar fascia, the iliac crest and the lateral two-thirds of the inguinal ligament and inserting onto the inferior border of the lower 3 - 4 ribs, the linea alba, the pubic crest and pectineal line.
Transversus abdominis
The transversus abdominis is the innermost of the flat anterior abdominal muscles, lying deep to the internal oblique. It originates from the thoracolumbar fascia, the iliac crest, the lateral one-third of the inguinal ligament and the 7th - 12th costal cartilages and inserts onto the linea alba, the pubic crest and the pectineal line.
Rectus abdominis
The rectus abdominis is a long muscle that extends the length of the anterior abdominal wall. It originates from the pubic crest, pubic tubercle and pubic symphysis and inserts onto the costal cartilages of ribs 5 - 7 and to the xiphoid process. It is a paired muscle, separated in the midline by the linea alba.
Function
The abdominal wall muscles form a firm, but flexible wall that keeps the abdominal viscera within the abdominal cavity, protects the viscera from injury and helps maintain the position of the viscera in the erect posture against the action of gravity.
The muscles act together to flex and rotate the vertebral column.
In addition, contraction of these muscles assists in forced expiration, and in coughing and vomiting, by pushing the viscera upwards. All of these muscles are involved in any action that increases intra-abdominal pressure, including childbirth, micturition and defaecation.
Innervation
The anterior abdominal wall muscles are innervated by the anterior rami of T7 - T12 and L1.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

