
Physiology
Gastrointestinal
Regarding fat digestion, which of the following statements is CORRECT:
Answer:
Fats are digested almost entirely in the small intestine and are only released from the stomach into the duodenum at the rate at which they can be digested (the presence of fatty acids and monoglycerides in the duodenum inhibits gastric emptying). In the duodenum fat is emulsified by bile acids, a process where larger lipid droplets are broken down into much smaller droplets providing a greater surface area for enzymatic digestion. Pancreatic lipase digests triglyceride into monoglycerides and free fatty acids. The products of fat digestion (fatty acids and monoglycerides), cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins diffuse passively into the enterocytes. Once inside the epithelial cell, lipid is taken into the smooth endoplasmic reticulum where much of it is re esterified. Dietary and synthesised lipids are then incorporated into chylomicrons in the Golgi body, which are exocytosed from the basolateral membrane to enter lacteals.Fat Handling
Physiology / Gastrointestinal / Small Intestine
Last Updated: 29th July 2024
Dietary Fat
Dietary fat is chiefly composed of triglycerides (esters of free fatty acids and glycerol which may be saturated or unsaturated). The essential fatty acids are linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, which cannot be manufactured in the body. The body is efficient at manufacturing fats (triglycerides, sterols and phospholipids) and will lay down subcutaneous fat stores. Dietary fat provides 37 kJ (9 kcal) of energy per gram. Fats are digested almost entirely in the small intestine and are only released from the stomach into the duodenum at the rate at which they can be digested.
Fat Digestion
Lingual and gastric lipase begin the hydrolysis of triglycerides (although this is not physiologically significant unless pancreatic lipase is deficient).
In the duodenum fat is emulsified by bile acids, a process where larger lipid droplets are broken down into much smaller droplets providing a greater surface area for enzymatic digestion. Pancreatic lipase digests triglycerides into monoglycerides and free fatty acids. These breakdown products form tiny particles with the bile acids called micelles.
Micelles are arranged so that hydrophobic lipid molecules lie in the centre, surrounded by bile acids arranged such the outer region is hydrophilic. This arrangement allows the micelles to enter the aqueous layers surrounding the microvilli, and the products of fat digestion (fatty acids and monoglycerides), cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins can then diffuse passively into the enterocytes, leaving the bile salts within the lumen of the gut where they are reabsorbed from the ileum or excreted in faeces.
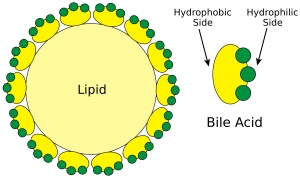
Structure of a Micelle. (Image by Bile1.png: Frank Boumphrey, MD derivative work: Hazmat2 (This file was derived from Bile1.png:) [CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Fat Absorption
Once inside the epithelial cell, lipid is taken into the smooth endoplasmic reticulum where much of it is re esterified. Dietary and synthesised lipids are then incorporated into chylomicrons in the Golgi body, which are exocytosed from the basolateral membrane to enter lacteals. Some small-chain fatty acids may be absorbed directly into the blood.

Fat Handling. (Image by OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Chylomicrons
From lacteals, chylomicrons pass into the lymphatic system and eventually reach the bloodstream via the thoracic duct. Chylomicrons consist mainly of triglyceride with small amounts of cholesterol and cholesteryl esters in the centre with a phospholipid coat studded with apolipoproteins.

Structure of a Chylomicron. (Image by AJC1 [Public Domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

