
Physiology
Gastrointestinal
Regarding carbohydrate digestion, which of the following statements is CORRECT:
Answer:
The monosaccharides are transported across the apical membrane of the enterocyte by means of cotransporter molecules, such as the sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT-1), that link their inward movement with that of Na+ down its concentration gradient. At the basolateral membrane, monosaccharides leave the cell either by simple or facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient and enter the circulation via the rich capillary network in the villus. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth; starch is initially hydrolysed by alpha-amylase produced in saliva and later by the pancreas to produce maltose, maltotriose and limit dextrins with short branches.Carbohydrate Handling
Physiology / Gastrointestinal / Small Intestine
Last Updated: 26th July 2024
Carbohydrates are the main energy source of most diets. They provide 17 kJ (4 kcal) of energy per gram. Carbohydrate is digested in the mouth and small intestine.
Dietary Carbohydrate
Most dietary carbohydrate is in the form of polysaccharides. The principal ingested polysaccharides are starch which is derived from plant sources and glycogen which is derived from animal sources. Other sources of carbohydrate are monosaccharides (glucose, fructose and galactose) and disaccharides (maltose, sucrose and lactose).
Dietary fibre consists of indigestible carbohydrate (found in plant foods) such as cellulose, lignin and pectin. Although it does not provide energy, fibre adds bulk to the bowel contents and increases gut motility (and decreases absorption of toxic compounds due to its binding properties, including some carcinogens).
Carbohydrate Digestion
Polysaccharides are digested by amylases, produced initially by salivary glands and later by the pancreas, to produce maltose, maltotriose and limit dextrins with short branches. These are broken down further by enzymes released from the intestinal brush border (maltase, isomaltase, sucrase and lactase) into the final products of carbohydrate digestion, the monosaccharides (glucose, fructose and galactose), which can be absorbed by the enterocyte.
The monosaccharides are transported across the apical membrane of the enterocyte by means of cotransporter molecules, such as the sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT-1), that link their inward movement with that of Na+ down its concentration gradient (the Na+ gradient being maintained by the Na+/K+ ATPase pump). At the basolateral membrane, monosaccharides leave the cell either by simple or facilitated diffusion down the concentration gradient and enter the circulation via the rich capillary network in the villus.
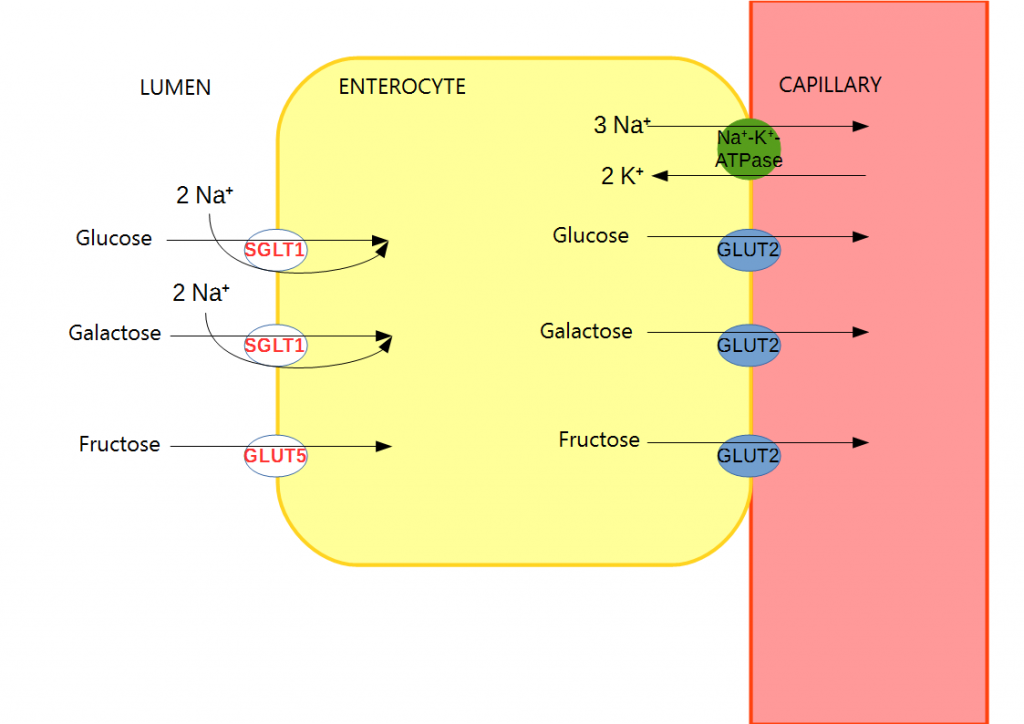
Carbohydrate Handling. (Image by Sonabi (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

