
Physiology
Renal
Which of the following is a response to increased sympathetic innervation to the kidney following a fall in extracellular volume:
Answer:
Increased sympathetic stimulation in response to a fall in extracellular volume causes:- peripheral vasoconstriction increasing the total peripheral resistance
- renal vasoconstriction decreasing the GFR
- stimulation of ADH release increasing water reabsorption
- stimulation of granular cells to release renin
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Physiology / Renal / Mechanism of Filtration
Last Updated: 26th July 2024
As plasma osmolality is strongly regulated by the osmoreceptors and ADH, changes in the major osmotic component of extracellular fluid, i.e. Na+, will result in changes in extracellular volume. The control of total body Na+ content by the kidney is therefore the main regulator of body fluid volume.
Sensing Blood Volume
Atrial and other cardiopulmonary stretch receptors detect a fall in central venous pressure (CVP) which reflects the blood volume. A fall in blood volume sufficient to reduce the blood pressure activates the baroreceptor reflex.
In both cases, increased sympathetic stimulation causes:
- peripheral vasoconstriction increasing the total peripheral resistance
- renal vasoconstriction decreasing the GFR
- stimulation of ADH release increasing water reabsorption
- stimulation of granular cells to release renin
Renin
Renin is produced by granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus and released in response to:
- A fall in extracellular fluid volume, central venous pressure or arterial blood pressure
- Decreased perfusion pressure and thus wall tension in the renal afferent arterioles
- Decreased tubular NaCl concentration detected by the cells of the macula densa
- A reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Renin cleaves plasma angiotensinogen (produced in the liver) into angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is converted by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) on pulmonary endothelial cells to angiotensin II.
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II is the primary hormone for Na+ homeostasis and has several important functions.
Angiotensin II acts to:
- Stimulate release of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex (which in turn acts to increase sodium reabsorption)
- Cause systemic vasoconstriction
- Cause vasoconstriction of the renal arterioles (predominant efferent effect thus intraglomerular pressure is stable or increased, thereby tending to maintain or even raise the GFR)
- Directly increase Na+ reabsorption from the proximal tubule (by activating Na+/H+ antiporters)
- Stimulate synthesis and release of ADH from the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary respectively
- Stimulate the sensation of thirst
- Potentiate sympathetic activity (positive feedback)
- Inhibit renin production by granular cells (negative feedback)
Aldosterone
Aldosterone acts mainly at the renal distal convoluted tubule (DCT) to cause sodium retention and potassium loss. It increases the synthesis of transport mechanisms in the distal nephron including the Na+ pump, Na+/H+ symporter, and Na+ and K+ channels in principal cells, and H+ ATPase in intercalated cells. Na+ (and thus water) reabsorption and K+ and H+ secretion are thereby enhanced.
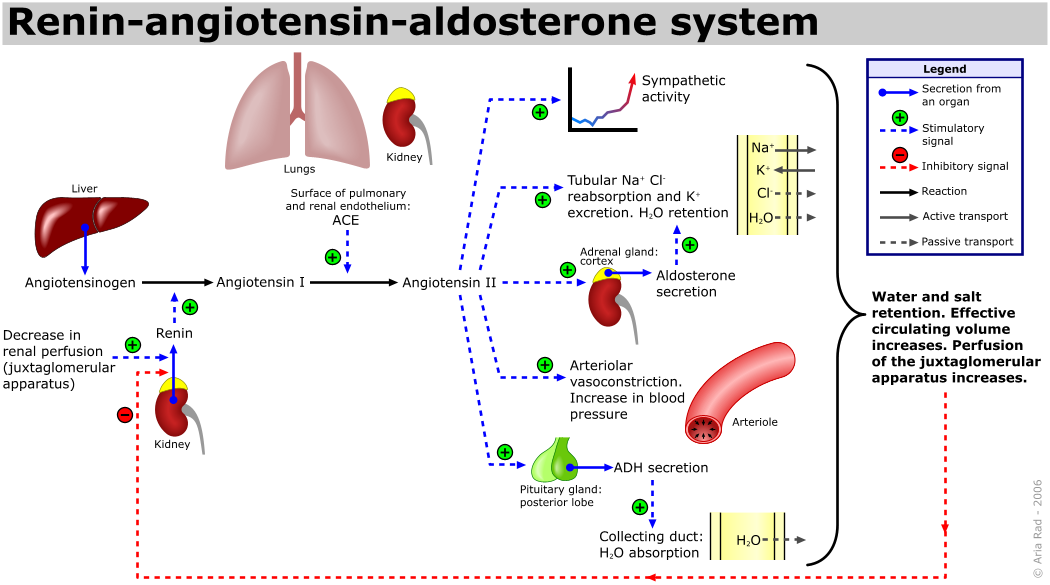
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. (Image by A. Rad (Own work) CC-BY-SA-3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

