
Anatomy
Abdomen
The stomach lies anterior to all of the following structures EXCEPT for the:
Answer:
The left lobe of the liver lies anterior to the stomach.Stomach
Anatomy / Abdomen / Gastrointestinal Tract
Last Updated: 4th July 2021
The stomach is the most dilated part of the gastrointestinal tract and has a J-like shape. The stomach is in the epigastric, umbilical and left hypochondrial regions of the abdomen. It is an intraperitoneal organ.
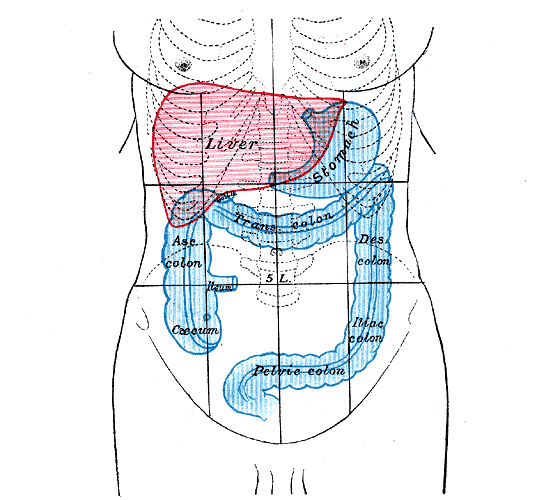
Surface Markings of the Stomach. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Anatomical Distinctions
The stomach is divided into four regions:
- the cardia which surrounds the opening of the oesophagus into the stomach
- the fundus which is the area above the level of the cardiac orifice
- the body which is the largest central region of the stomach
- the pyloric part which is divided into the pyloric antrum and the pyloric canal which opens into the duodenum.
The most distal portion of the pyloric canal contains a thickened ring of gastric circular muscle, the pyloric sphincter that surrounds the distal pyloric orifice. The pyloric orifice is just to the right of the midline in the transpyloric plane. The pyloric sphincter controls the exit of chyme from the stomach into the duodenum. The sphincter is constricted by sympathetic stimulation and relaxed by parasympathetic action. Parasympathetic fibres in the vagus nerve are also secretomotor to gastric glands and motor to muscular wall of stomach.
![Modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://mrcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Stomach.png)
Stomach. (Image modified by FRCEM Success. Original by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Relations
The stomach lies inferior to the diaphragm.
The stomach lies posterior to:
- the anterior abdominal wall
- the left costal margin
- the left lobe of the liver
The stomach lies anterior to the stomach bed formed by:
- the diaphragm
- the pancreas
- the transverse mesocolon
- the left colic flexure
- the left kidney
- the left adrenal gland
- the spleen
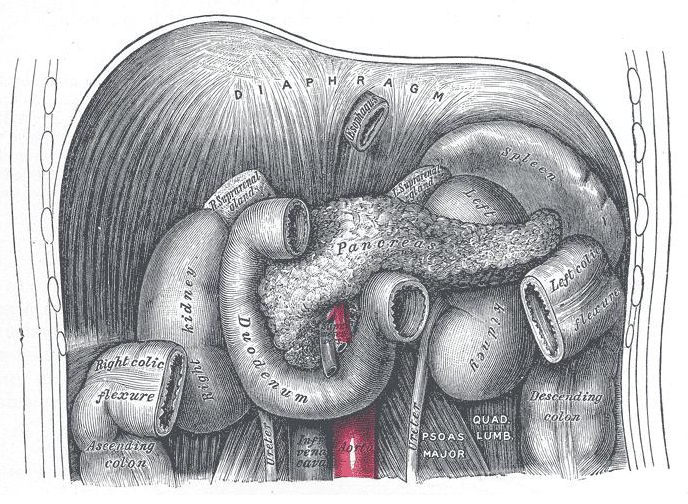
Relations of the Stomach. (Image by Henry Vandyke Carter [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons)
Blood supply
The arterial supply to the stomach is derived from all three branches (left gastric, splenic and common hepatic branches) of the coeliac trunk.
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

