
Anatomy
Abdomen
Regarding the penis, which of the following statements is CORRECT:
Answer:
Because the anatomical position of the penis is erect, the paired corpora cavernosa are defined as dorsal in the body of the penis and the single corpus spongiosum as ventral. The nerves and vessels lie superficial to the corpus cavernosum. The urethra lies within the corpus spongiosum.Penis and Scrotum
Anatomy / Abdomen / Male Reproductive System
Last Updated: 27th February 2020
Penis
STRUCTURE:
The penis is composed mainly of three masses of erectile tissue: the paired corpora cavernosa and the single corpus spongiosum, which contains the spongy urethra.
Because the anatomical position of the penis is erect, the paired corpora cavernosa are defined as dorsal in the body of the penis and the single corpus spongiosum as ventral. The nerves and vessels lie superficial to the corpus cavernosum. The urethra lies within the corpus spongiosum.
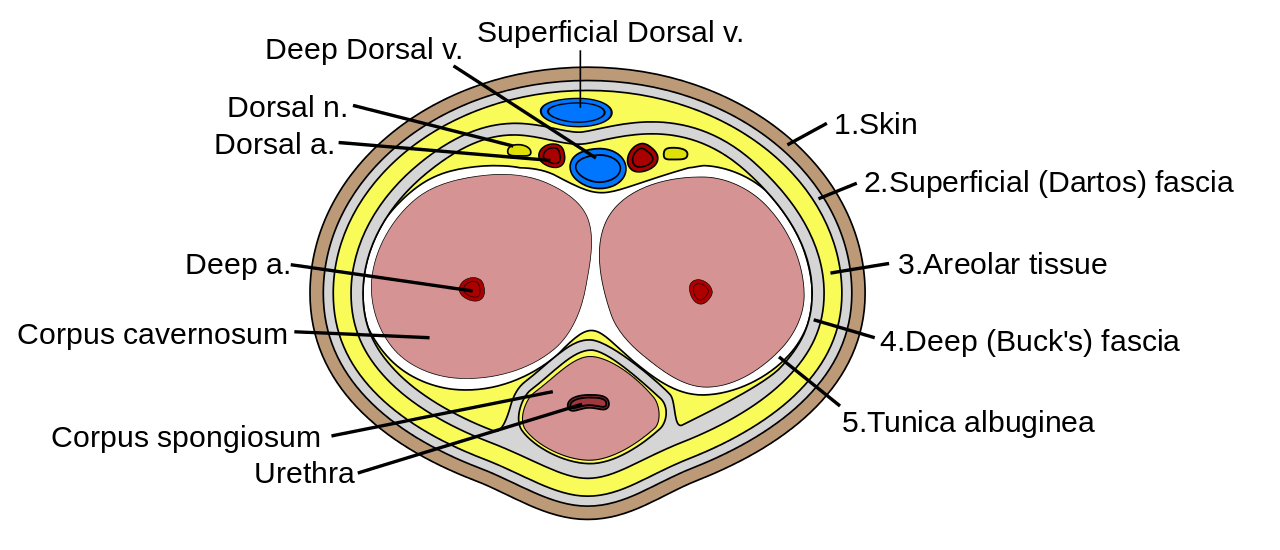
Cross-section of the Penis. (Image by Mcstrother (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
INNERVATION:
The nerves supplying the penis are derived from the S2 - S4 spinal cord segments and spinal ganglia, passing through the pelvic splanchnic and pudendal nerves respectively. Sensory and sympathetic innervation is provided primarily by the dorsal nerve of the penis, a terminal branch of the pudendal nerve. Branches of the ilioinguinal nerve supply skin at the root of the penis.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
The lymphatics from the penile skin and prepuce run proximally to join the lymphatics from the scrotum and perineum draining into the superficial inguinal nodes, especially the superomedial group. The lymphatics from the glans and penile urethra drain primarily into the deep inguinal nodes.
Scrotum
INNERVATION:
The scrotum is innervated by nerves derived primarily from spinal roots L1 and S2 - S3:
- anterolaterally by the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve (L1 - L2)Penis and Scrotum,
- anteriorly by scrotal branches of the ilioinguinal nerve (L1)
- posteriorly by scrotal branches of the perineal nerve of the pudendal nerve (S3)
- inferiorly by perineal branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S2)
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE:
The lymph drainage of the scrotum is to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes (in contrast to that of the testes which is to the lumbar (para-aortic) nodes in the abdomen).
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

