
Anatomy
Central Nervous System
Which of the following clinical features is most suggestive of a lesion of the occipital lobe:
Answer:
Homonymous hemianopia is most likely caused by damage to the occipital lobe.Occipital Lobe
Anatomy / Central Nervous System
Last Updated: 11th April 2019
The occipital lobe rests inferiorly upon the tentorium cerebelli which segregates the cerebrum from the cerebellum. The parieto-occipital sulcus separates the occipital lobe from the parietal and temporal lobes anteriorly.
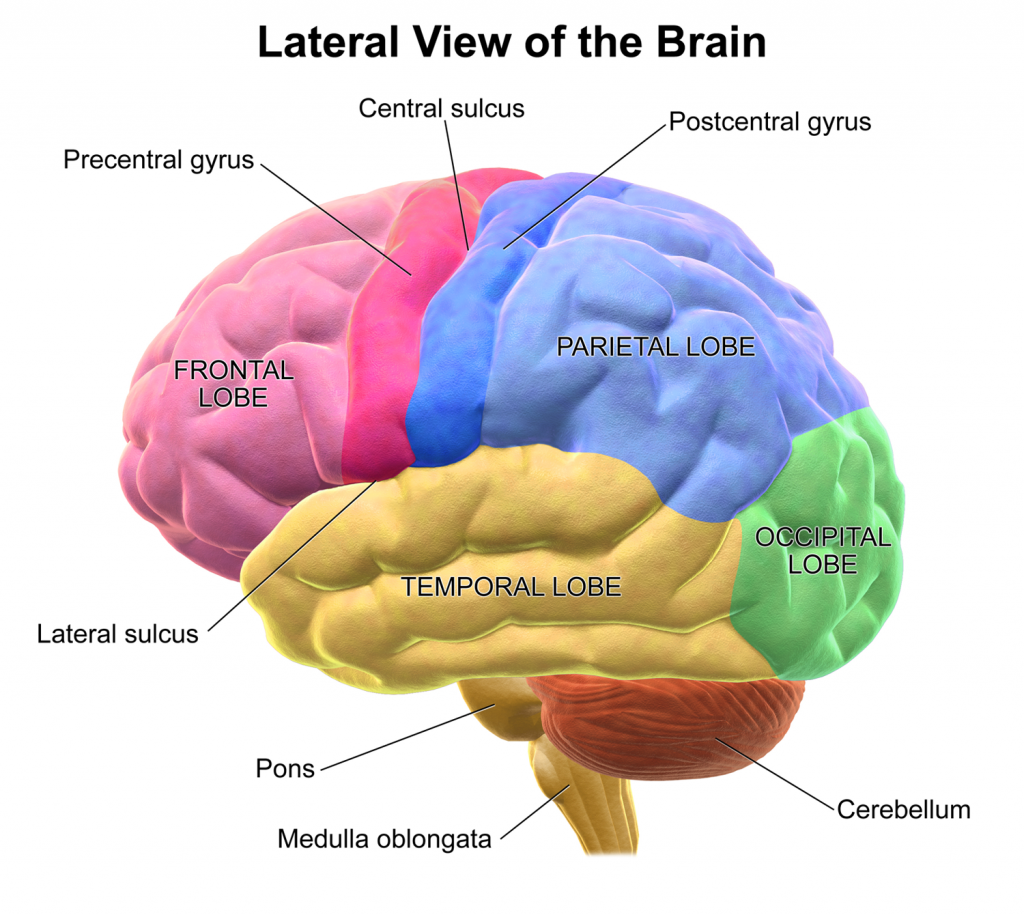
Lobes of the Brain. (Image by BruceBlaus (Own work) [CC BY 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Cortical Areas
The primary visual cortex is located within the occipital lobe and together with the visual association cortex is responsible for vision.
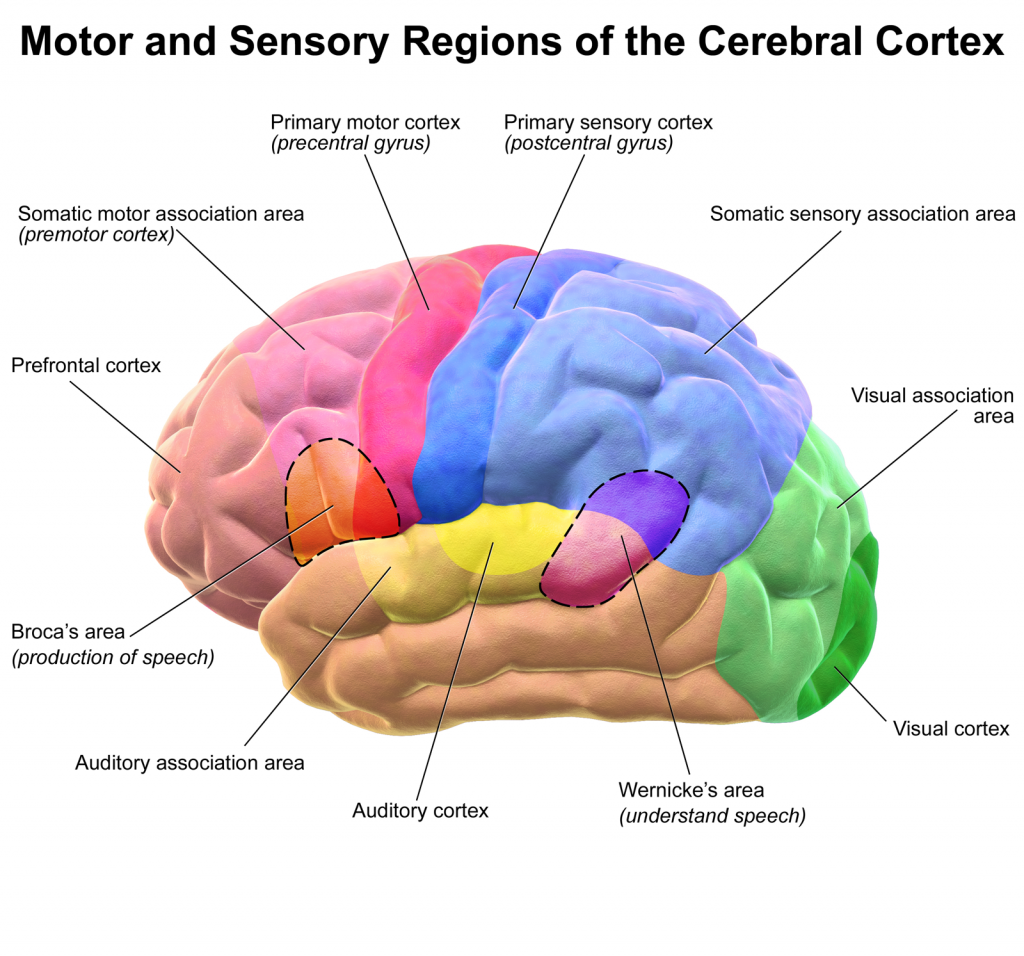
Motor and Sensory Regions of the Cerebral Cortex. (Image by Blausen.com staff. “Blausen gallery 2014, via Wikimedia Commons)
Blood Supply
The blood supply to the occipital lobe is from the posterior cerebral artery, but the occipital poles, serving macular vision, have additional supply from a branch of the middle cerebral artery.
![By derivative work: Frank Gaillard (talk) Brain_stem_normal_human.svg: Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Brain_stem_normal_human.svg) [GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or CC BY 2.5 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://primary-cdn.frcemsuccess.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Cerebral-Vascular-Territories-1-1.jpg)
Cerebral Blood Supply. (Image by derivative work: Frank Gaillard (talk) Brain_stem_normal_human.svg: Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Brain_stem_normal_human.svg) [GFDL 1.3 (www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl-1.3.html), via Wikimedia Commons)
Clinical Implications
Damage to the occipital lobe can result in:
- Contralateral homonymous hemianopia (with macular sparing)
- Cortical blindness
- Visual agnosia
- Colour blindness
- Visual illusions or hallucinations
- Difficulty reading and writing
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |

