← Back to Session
Questions Answered: 233
Final Score 90%
210
23
Questions
- Q1. ✓ Correct
- Q2. ✓ Correct
- Q3. X Incorrect
- Q4. ✓ Correct
- Q5. ✓ Correct
- Q6. ✓ Correct
- Q7. ✓ Correct
- Q8. ✓ Correct
- Q9. ✓ Correct
- Q10. ✓ Correct
- Q11. ✓ Correct
- Q12. ✓ Correct
- Q13. ✓ Correct
- Q14. ✓ Correct
- Q15. ✓ Correct
- Q16. ✓ Correct
- Q17. ✓ Correct
- Q18. ✓ Correct
- Q19. ✓ Correct
- Q20. ✓ Correct
- Q21. ✓ Correct
- Q22. ✓ Correct
- Q23. ✓ Correct
- Q24. ✓ Correct
- Q25. ✓ Correct
- Q26. ✓ Correct
- Q27. ✓ Correct
- Q28. ✓ Correct
- Q29. ✓ Correct
- Q30. ✓ Correct
- Q31. ✓ Correct
- Q32. ✓ Correct
- Q33. ✓ Correct
- Q34. ✓ Correct
- Q35. ✓ Correct
- Q36. ✓ Correct
- Q37. ✓ Correct
- Q38. ✓ Correct
- Q39. ✓ Correct
- Q40. ✓ Correct
- Q41. ✓ Correct
- Q42. ✓ Correct
- Q43. ✓ Correct
- Q44. ✓ Correct
- Q45. X Incorrect
- Q46. ✓ Correct
- Q47. X Incorrect
- Q48. ✓ Correct
- Q49. ✓ Correct
- Q50. ✓ Correct
- Q51. ✓ Correct
- Q52. ✓ Correct
- Q53. ✓ Correct
- Q54. X Incorrect
- Q55. ✓ Correct
- Q56. ✓ Correct
- Q57. ✓ Correct
- Q58. ✓ Correct
- Q59. ✓ Correct
- Q60. ✓ Correct
- Q61. ✓ Correct
- Q62. ✓ Correct
- Q63. ✓ Correct
- Q64. ✓ Correct
- Q65. ✓ Correct
- Q66. ✓ Correct
- Q67. ✓ Correct
- Q68. ✓ Correct
- Q69. ✓ Correct
- Q70. ✓ Correct
- Q71. ✓ Correct
- Q72. ✓ Correct
- Q73. ✓ Correct
- Q74. ✓ Correct
- Q75. ✓ Correct
- Q76. X Incorrect
- Q77. ✓ Correct
- Q78. ✓ Correct
- Q79. ✓ Correct
- Q80. ✓ Correct
- Q81. ✓ Correct
- Q82. ✓ Correct
- Q83. ✓ Correct
- Q84. ✓ Correct
- Q85. ✓ Correct
- Q86. ✓ Correct
- Q87. X Incorrect
- Q88. ✓ Correct
- Q89. ✓ Correct
- Q90. ✓ Correct
- Q91. X Incorrect
- Q92. ✓ Correct
- Q93. ✓ Correct
- Q94. ✓ Correct
- Q95. ✓ Correct
- Q96. ✓ Correct
- Q97. ✓ Correct
- Q98. ✓ Correct
- Q99. X Incorrect
- Q100. ✓ Correct
- Q101. X Incorrect
- Q102. ✓ Correct
- Q103. ✓ Correct
- Q104. ✓ Correct
- Q105. ✓ Correct
- Q106. ✓ Correct
- Q107. ✓ Correct
- Q108. ✓ Correct
- Q109. ✓ Correct
- Q110. ✓ Correct
- Q111. ✓ Correct
- Q112. ✓ Correct
- Q113. ✓ Correct
- Q114. ✓ Correct
- Q115. ✓ Correct
- Q116. ✓ Correct
- Q117. ✓ Correct
- Q118. ✓ Correct
- Q119. ✓ Correct
- Q120. ✓ Correct
- Q121. ✓ Correct
- Q122. X Incorrect
- Q123. ✓ Correct
- Q124. ✓ Correct
- Q125. ✓ Correct
- Q126. ✓ Correct
- Q127. ✓ Correct
- Q128. ✓ Correct
- Q129. ✓ Correct
- Q130. ✓ Correct
- Q131. ✓ Correct
- Q132. ✓ Correct
- Q133. ✓ Correct
- Q134. ✓ Correct
- Q135. ✓ Correct
- Q136. ✓ Correct
- Q137. ✓ Correct
- Q138. ✓ Correct
- Q139. X Incorrect
- Q140. ✓ Correct
- Q141. ✓ Correct
- Q142. ✓ Correct
- Q143. ✓ Correct
- Q144. ✓ Correct
- Q145. ✓ Correct
- Q146. ✓ Correct
- Q147. ✓ Correct
- Q148. ✓ Correct
- Q149. ✓ Correct
- Q150. X Incorrect
- Q151. ✓ Correct
- Q152. ✓ Correct
- Q153. ✓ Correct
- Q154. ✓ Correct
- Q155. ✓ Correct
- Q156. ✓ Correct
- Q157. ✓ Correct
- Q158. ✓ Correct
- Q159. ✓ Correct
- Q160. ✓ Correct
- Q161. ✓ Correct
- Q162. X Incorrect
- Q163. ✓ Correct
- Q164. ✓ Correct
- Q165. ✓ Correct
- Q166. ✓ Correct
- Q167. ✓ Correct
- Q168. ✓ Correct
- Q169. X Incorrect
- Q170. ✓ Correct
- Q171. ✓ Correct
- Q172. ✓ Correct
- Q173. ✓ Correct
- Q174. ✓ Correct
- Q175. ✓ Correct
- Q176. ✓ Correct
- Q177. ✓ Correct
- Q178. ✓ Correct
- Q179. ✓ Correct
- Q180. X Incorrect
- Q181. ✓ Correct
- Q182. ✓ Correct
- Q183. X Incorrect
- Q184. ✓ Correct
- Q185. X Incorrect
- Q186. ✓ Correct
- Q187. ✓ Correct
- Q188. X Incorrect
- Q189. X Incorrect
- Q190. ✓ Correct
- Q191. X Incorrect
- Q192. ✓ Correct
- Q193. ✓ Correct
- Q194. ✓ Correct
- Q195. ✓ Correct
- Q196. ✓ Correct
- Q197. ✓ Correct
- Q198. ✓ Correct
- Q199. ✓ Correct
- Q200. ✓ Correct
- Q201. ✓ Correct
- Q202. ✓ Correct
- Q203. ✓ Correct
- Q204. X Incorrect
- Q205. X Incorrect
- Q206. ✓ Correct
- Q207. ✓ Correct
- Q208. ✓ Correct
- Q209. X Incorrect
- Q210. ✓ Correct
- Q211. ✓ Correct
- Q212. ✓ Correct
- Q213. ✓ Correct
- Q214. ✓ Correct
- Q215. ✓ Correct
- Q216. ✓ Correct
- Q217. ✓ Correct
- Q218. ✓ Correct
- Q219. ✓ Correct
- Q220. ✓ Correct
- Q221. ✓ Correct
- Q222. ✓ Correct
- Q223. ✓ Correct
- Q224. ✓ Correct
- Q225. ✓ Correct
- Q226. ✓ Correct
- Q227. ✓ Correct
- Q228. ✓ Correct
- Q229. ✓ Correct
- Q230. ✓ Correct
- Q231. ✓ Correct
- Q232. ✓ Correct
- Q233. ✓ Correct
- Q234. Skipped

Anatomy
Upper Limb
Question 217 of 234
A 16 year old girl presents complaining of weakness of her left hand following an injury to her left arm. On examination she has weakness of flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the ring finger, and inability to adduct that same finger. Which of the following muscles is most likely affected:
Answer:
The interossei muscles assist the lumbricals with flexion of the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints. The palmar interossei cause adduction of the fingers and the dorsal interossei cause abduction of the fingers. The flexor digitorum profundus and superficialis are involved in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joint but have no function in adduction of the fingers.Hand Movements
Anatomy / Upper Limb / Wrist and Hand
Last Updated: 29th January 2019
Hand movements are complex. The table below shows an overview of hand and thumb movements and the main muscles bringing about these movements.
Table: Movements of the Finger Joints
| Finger Movements | Primary Muscle (Assisting Muscles) | Primary Nerve (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexion of MCPJ of digits 2 – 5 | Lumbricals (flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor digiti minimi, interossei) | Median and ulnar |
| Flexion of PIPJ of digits 2 – 5 | Flexor digitorum superficialis (flexor digitorum profundus) | Median |
| Flexion of DIPJ of digits 2 – 5 | Flexor digitorum profundus | Median and ulnar |
| Extension of MCPJ of digits 2 – 5 | Extensor digitorum, extensor indicis, extensor digiti minimi | Radial |
| Extension of PIPJ and DIPJ of digits 2 – 5 | Lumbricals and interossei (extensor digitorum) | Ulnar and median |
| Adduction of digits 2 – 5 | Palmar interossei | Ulnar |
| Abduction of digits 2 – 4 | Dorsal interossei | Ulnar |
| Abduction of little finger | Abductor digiti minimi | Ulnar |
| Opposition of little finger | Opponens digiti minimi | Ulnar |
Table: Movement of the Thumb Joints
| Thumb Movements | Primary Muscle(s) | Nerve Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Flexion of thumb at MCPJ | Flexor pollicis longus and brevis | Median and ulnar |
| Flexion of thumb at IPJ | Flexor pollicis longus | Median |
| Extension of thumb at CMCJ and MCPJ | Extensor pollicis longus and brevis | Radial |
| Extension of thumb at IPJ | Extensor pollicis longus | Radial |
| Abduction of thumb | Abductor pollicis longus and brevis | Radial and median |
| Adduction of thumb | Adductor pollicis | Ulnar |
| Opposition of thumb | Opponens pollicis | Median |
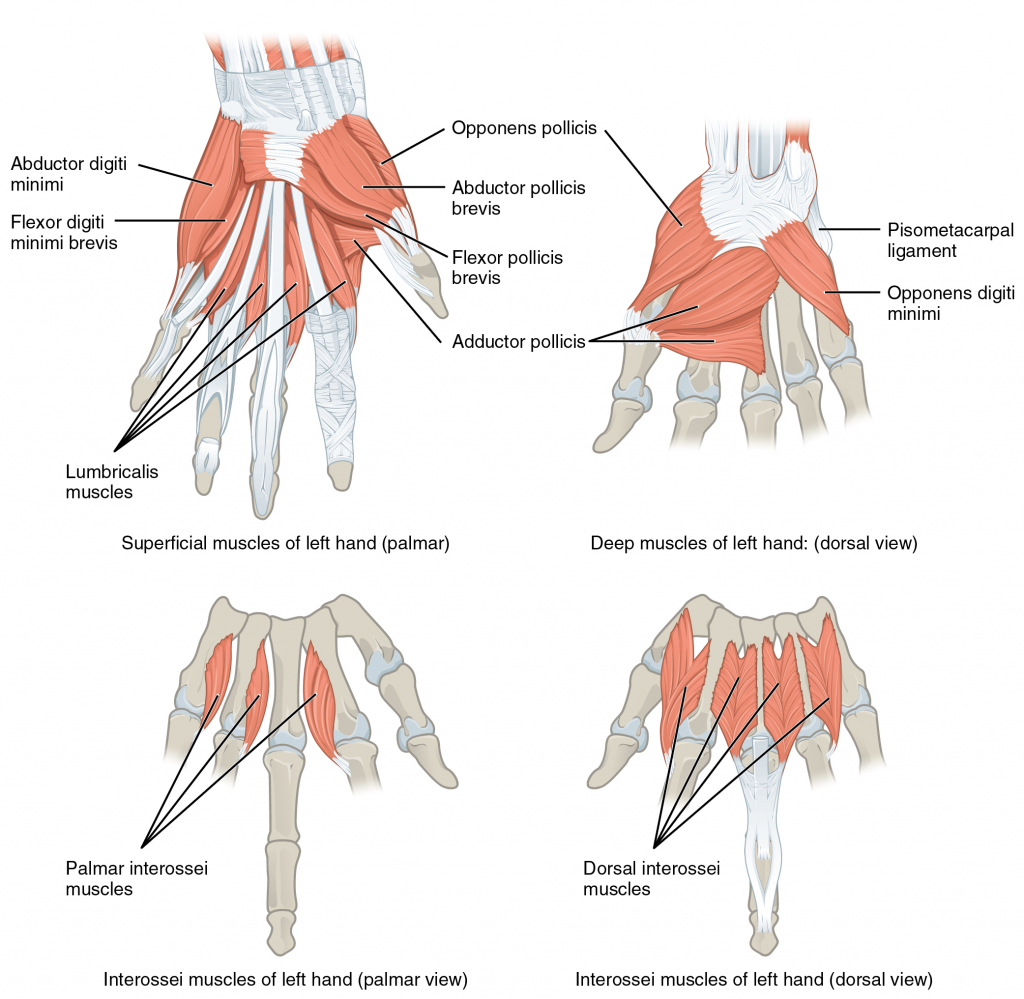
Muscles of the Hand. (Image by OpenStax [CC BY 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons)
Report A Problem
Is there something wrong with this question? Let us know and we’ll fix it as soon as possible.
Loading Form...
- Biochemistry
- Blood Gases
- Haematology
| Biochemistry | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 135 – 145 mmol/l |
| Potassium | 3.0 – 4.5 mmol/l |
| Urea | 2.5 – 7.5 mmol/l |
| Glucose | 3.5 – 5.0 mmol/l |
| Creatinine | 35 – 135 μmol/l |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 5 – 35 U/l |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT) | < 65 U/l |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 30 – 135 U/l |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | < 40 U/l |
| Total Protein | 60 – 80 g/l |
| Albumin | 35 – 50 g/l |
| Globulin | 2.4 – 3.5 g/dl |
| Amylase | < 70 U/l |
| Total Bilirubin | 3 – 17 μmol/l |
| Calcium | 2.1 – 2.5 mmol/l |
| Chloride | 95 – 105 mmol/l |
| Phosphate | 0.8 – 1.4 mmol/l |
| Haematology | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 11.5 – 16.6 g/dl |
| White Blood Cells | 4.0 – 11.0 x 109/l |
| Platelets | 150 – 450 x 109/l |
| MCV | 80 – 96 fl |
| MCHC | 32 – 36 g/dl |
| Neutrophils | 2.0 – 7.5 x 109/l |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 – 4.0 x 109/l |
| Monocytes | 0.3 – 1.0 x 109/l |
| Eosinophils | 0.1 – 0.5 x 109/l |
| Basophils | < 0.2 x 109/l |
| Reticulocytes | < 2% |
| Haematocrit | 0.35 – 0.49 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width | 11 – 15% |
| Blood Gases | Normal Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.35 – 7.45 |
| pO2 | 11 – 14 kPa |
| pCO2 | 4.5 – 6.0 kPa |
| Base Excess | -2 – +2 mmol/l |
| Bicarbonate | 24 – 30 mmol/l |
| Lactate | < 2 mmol/l |
Are you sure you wish to end this session?

